Thyroidectomy
Home / Procedure Detail
Thyroidectomy
- Procedure
- Thyroidectomy
Thyroidectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of your thyroid gland. Your thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of your neck. It makes hormones that control every part of your metabolism, from your heart rate to how quickly you burn calories.
Healthcare providers perform thyroidectomy to treat thyroid disorders. These include cancer, a noncancerous enlargement of the thyroid (goiter), and overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism).
How much of your thyroid gland is removed during thyroidectomy depends on the reason for the surgery. If you need only part of your thyroid removed (partial thyroidectomy), your thyroid may work normally after surgery. If you need your entire thyroid removed (total thyroidectomy), you need daily treatment with thyroid hormone to replace your thyroid’s natural function.
Procedure Primary Points
- Thyroidectomy removes part or all of the thyroid gland.
- It treats thyroid disorders like cancer, goiter, and hyperthyroidism.
- The extent of gland removal varies based on the reason.
- Partial thyroidectomy allows normal thyroid function post-surgery.
- Total thyroidectomy requires daily hormone treatment for function replacement.
Why it's done
Your doctor may recommend thyroidectomy if you have conditions such as:
- Thyroid cancer. Cancer is the most common reason for thyroidectomy. If you have thyroid cancer, removing most or all of your thyroid will likely be a treatment option.
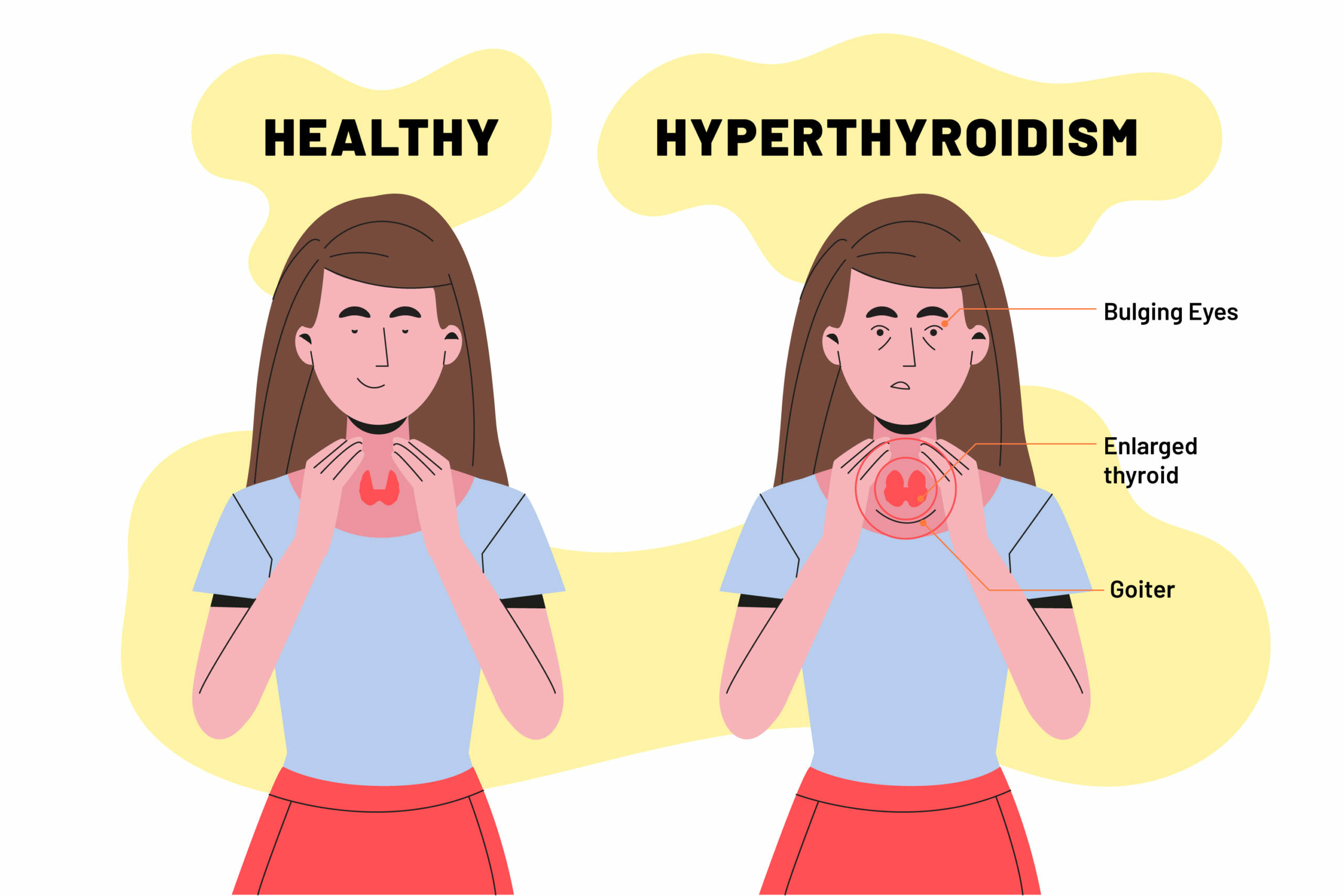
- Noncancerous enlargement of the thyroid (goiter). Removing all or part of your thyroid gland may be an option for a large goiter. A large goiter may be uncomfortable or make it hard to breathe or swallow. A goiter may also be removed if it’s causing your thyroid to be overactive.
- Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). In hyperthyroidism, your thyroid gland produces too much of the hormone thyroxine. Thyroidectomy may be an option if you have problems with anti-thyroid drugs, or if you don’t want radioactive iodine therapy. These are two other common treatments for hyperthyroidism.
- Suspicious thyroid nodules. Some thyroid nodules can’t be identified as cancerous or noncancerous after testing a sample from a needle biopsy. If your nodules are at increased risk of being cancerous, you may be a candidate for thyroidectomy.
Medical Procedures
MedEx did help me a lot not only for connecting with clinics but also for other miscellaneous items such as visa extention. I am really sastify with the services received from MedEx. I've recommended to some of my friends to connect with MedEx too if they have plan to go for medical trip to BKK. 🙂
Engyin HtunSingapore 
Highly recommend to MedEx .They are professional and amazing team.
MedEx Staffs should have closed relationships with hospitals staffs to get more information and services.So,they can give the best services to patients.
Thomas FlyerMyanmar 
Owing to my heart pacemaker implant case, if I got a chance to refer anyone, without blinking my eyes I would refer to Vejthani Hospital. I am very grateful.
Bhagwan Ratna TuladharKathmandu, Nepal 
MedEx was very kind, patient, supportive and very helpful with my needs for seeing doctors and doing physical therapy here in Thailand. MedEx fulfilled everything I needed with my stay here with prompt actions, and I highly recommend MedEx if you are coming to Bangkok for medical treatment.
Ko Sai Aung Lwin TunMyanmar 










